L-HySEA (Landslide-HySEA)
| Code name | L-HySEA (Landslide-HySEA) |
| Developer(s) | Manuel J. Castro Díaz Jorge Macías Sánchez Marc de la Asunción Contact person: Jorge Macías Sánchez |
| Link | |
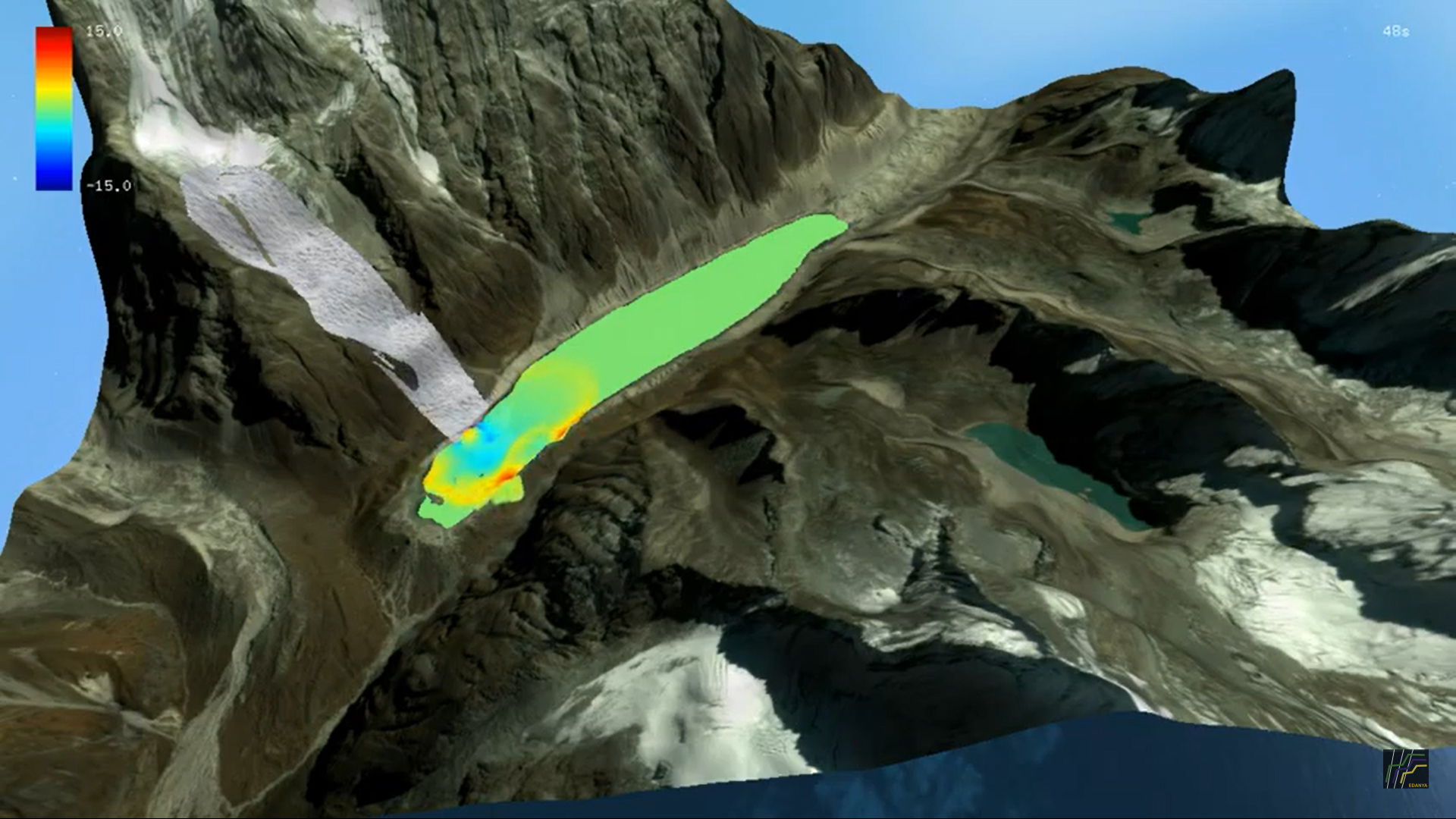
| Short description | L-HySEA solves the 2D shallow water equations on hydrostatic and dispersive versions. L-HySEA is based on a high-order Finite Volume (FV) discretization (hydrostatic) with Finite Differences (FD) for the dispersive version on two-way structured nested meshes in spherical coordinates. Initial conditions from the Okada model or initial deformation, synchronous and asynchronous multi-Okada, rectangular and triangular faults. |
| Original code level | 3 |
| Pilot(s) involved | |
| Main results and References | MAIN RESULTS:
REFERENCES: Macías, J., Vázquez, J.T., Fernández-Salas, L.M., González-Vida, J.M., Bárcenas, P., Castro, M.J., Díaz del Río, V., and Alonso, B. (2015). The Al-Boraní submarine landslide and associated tsunami. A modelling approach. Marine Geology, 361:79-95. [doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2014.12.006]. González-Vida, J.M., Macías, J., Castro, M.J., Sánchez-Linares, C., de la Asunción, M., Ortega, S., and Arcas, D. (2019). The Lituya Bay landslide-generated mega-tsunami. Numerical simulation and sensitivity analysis, Natural Hazards and Earth System Science, 19, 369-388 [doi: 10.5194/nhess-19-369-2019]. |
| Performance results |
|