A component of ChEESE´s pilot demonstrator on Geomagnetic Forecasts (PD11) comprises the simulation and analysis of geomagnetic reversals, which are exceptional periods in the Earth’s history when the magnetic North becomes South, and vice-versa. This is a process which occurred over the history of the Earth. Over the past 10 million years, there were about four to five such reversals per million years. The last reversal took place about 780,000 years ago, which indicates that the next one may be overdue. Since the paleomagnetic record of such events is sparse in both space and time, ChEESE will resort to numerical simulations to complement our description of reversals.
In order to better understand the nature of geomagnetic fields during a reversal, ChEESE is developing a workflow to analyse reversals simulated using the flagship code XSHELLS. These simulations have been running with an unprecedented level of turbulence due to the combined effects of careful survey of parameter space and improved code performance.
One of the questions that ChEESE wants to answer is how low geomagnetic intensity gets during a reversal. This is a question of practical interest, since magnetic fields shield us from solar wind, thereby limiting hazards for artificial satellites revolving around the Earth as well as spacecraft flying through the area.
To give you an idea, the figure below shows the intensity of the field in 2020, based on the recently released 13th generation of the international geomagnetic reference field (IGRF).
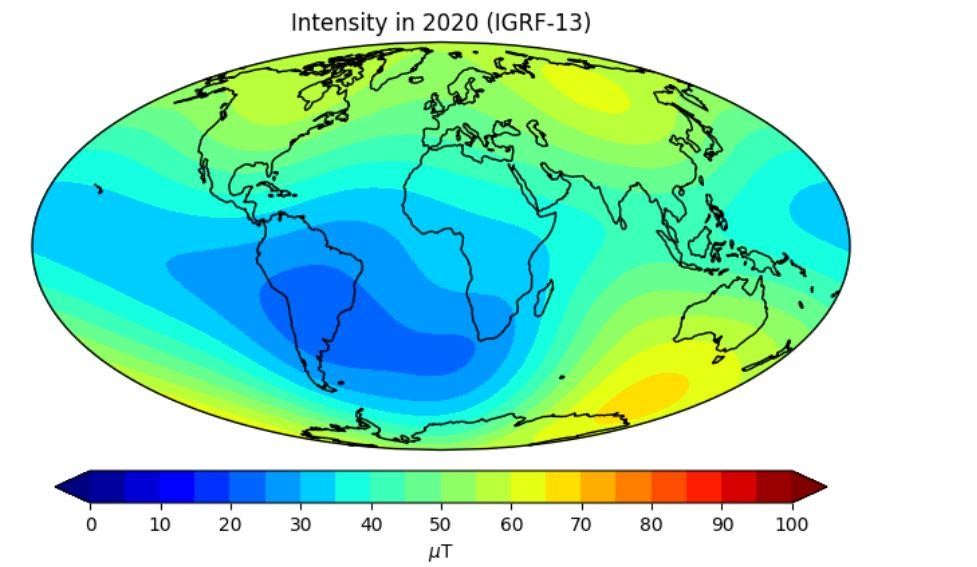
The intensity is stronger at high latitudes (this reflects the mostly dipolar character of the field generated by Earth in its liquid core via dynamo action); it can reach values as large as 75 microTesla (μT). There is a region of low intensity which is known as the south Atlantic anomaly, which is known to have a high level of satellite hazards. There the intensity is quite low (about 20 μT).
The video below shows how the intensity evolves during a reversal that ChEESE has simulated. The simulation was done using the flagship code XSHELLS run at a resolution of (336 x 213 x 170), which is, by far, the highest resolution reported to date for the simulation of a geomagnetic reversal. The integration with XSHELLS spans the equivalent of 3.5 million geophysical years (using national allocations). The full 3D analysis of the simulation has yet to be completed, but here is a teaser on how the intensity fluctuates during a simulated reversal.
In this video, the intensity is shown to the left. The right panel shows the vertical component of the magnetic field. Red means that the associated magnetic field lines are going inside the earth, and blue means that they are going outside the earth. The structure of the map of the vertical component reflects the fact that the field is mostly dipolar. The structure of the field becomes particular when the field flips - there is a section in the video where you will notice that both the intensity is weak (to the point that its maximum at that point in time in the simulation is lower than the present-day minimum) and the structure of the field is simultaneously multipolar - meaning that there are several North and South poles. It is precisely this transitional period which will be critical for us, if a reversal were to occur.
This video spans a time interval of about 20,000 years from its start to its end. The transitional period lasts for a few hundred years.


