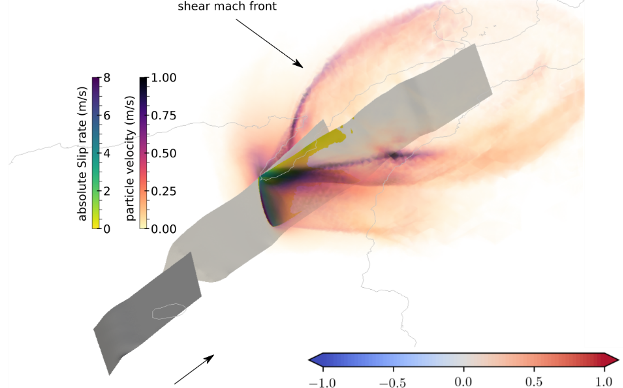
Within the ChEESE Center of Excellence for Exascale in Solid Earth (ChEESE), the earthquake simulation software SeisSol, one of the 10 ChEESE flagship codes, is being ported to GPU-based supercomputers. First simulations have now been executed on Marconi100 and Piz Daint, two of the largest European supercomputers.
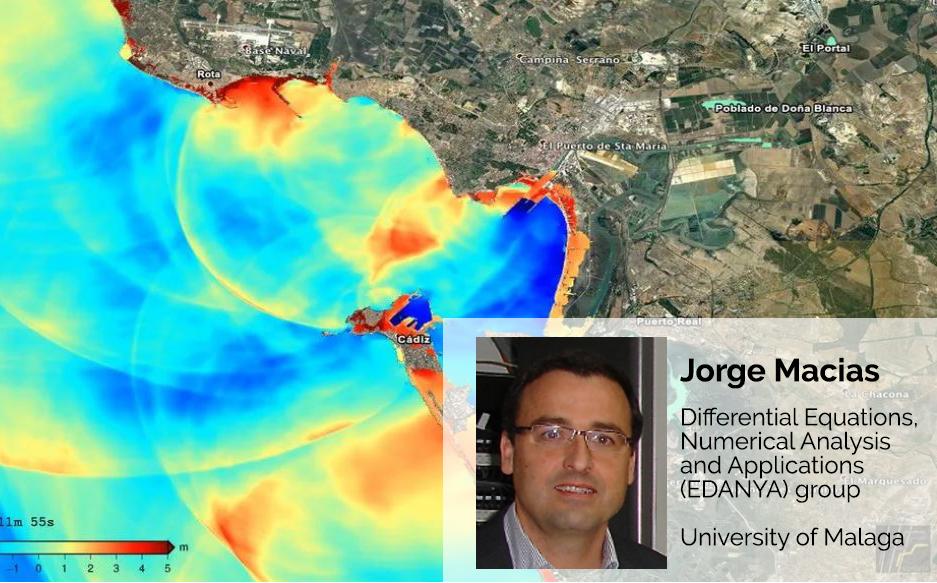
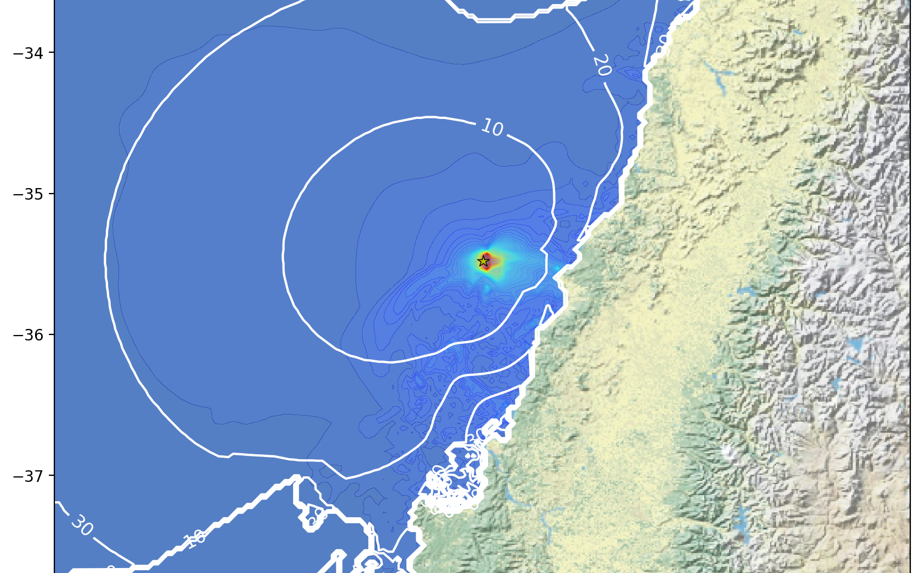
Jorge Macías is a researcher from the University of Malaga and a member of the Differential Equations, Numerical Analysis and Applications (EDANYA) group. EDANYA is an internationally renowned group in tsunami modelling and the developers of the Tsunami-HySEA code, a software used in predicting the behaviour and effects of tsunamis.
A component of ChEESE´s pilot demonstrator on Geomagnetic Forecasts (PD11) comprises the simulation and analysis of geomagnetic reversals, which are exceptional periods in the Earth’s history when the magnetic North becomes South, and vice-versa. This is a process which occurred over the history of the Earth. Over the past 10 million years, there were about four to five such reversals per million years. The last reversal took place about 780,000 years ago, which indicates that the next one may be overdue.
ChEESE has been awarded almost 110 million core hours to be used towards HPC-related research in earthquakes, volcanoes and tsunamis after winning 3 Project Access proposals in the 20th PRACE call. The allocated core hours will specifically be used to support several of ChEESE´s Exascale pilot demonstrators on seismic tomography, volcanic ash hazard and forecast and tsunami early warning.
February 11 is the International Day of Women and Girls in Science. In celebration of this special occasion, ChEESE would like to acknowledge the women scientists and support staff who are working to make the project a success.